By Dr.Ravindra Patil
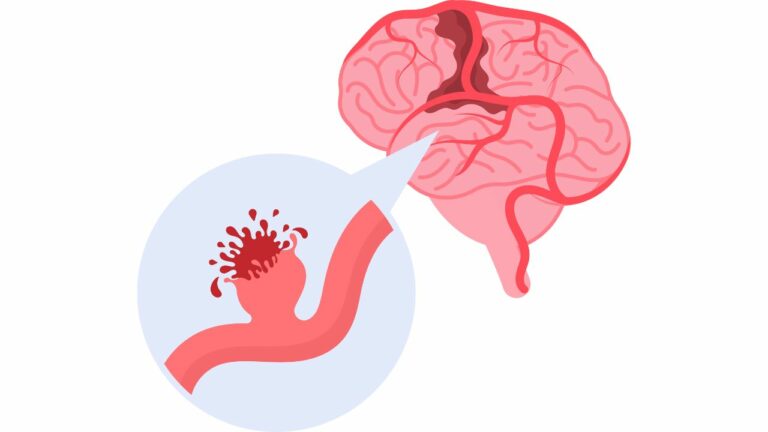
Cerebral vascular aneurysms, often referred to simply as brain aneurysms, occur when a weakened area in the blood vessel wall within the brain leads to a bulging or ballooning of the vessel. These aneurysms can develop anywhere in the brain and vary in size and shape. The worst thing that can occur in an aneurysm is that it can rupture. That causes cerebral haemorrhage and may lead to serious medical condition called cerebrovascular stroke or brain stroke.
Brain aneurysms often do not cause symptoms until they rupture. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, neck pain, blurred or double vision, sensitivity to light, and loss of consciousness. In the case of a ruptured aneurysm, symptoms can be severe and may include a sudden, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
Treatment options for cerebral vascular aneurysms depend on various factors, including the size and location of the aneurysm, as well as the individual’s overall health. Treatment options may include observation, medication to control symptoms and prevent complications, surgical clipping to prevent rupture, endovascular coiling to seal off the aneurysm, or a combination of these approaches. Remember, as cerebral aneurysms are inside the brain, any surgery or intervention to clip them or repair them may involve brain surgery, which itself is a very dangerous and risky procedure.
A ruptured brain aneurysm occurs when the weakened area in the blood vessel wall gives way, causing bleeding into the surrounding brain tissue. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent further damage and complications. The intracranial pressure [ICP] of such patients will rise and this will lead to many symptoms like
Signs of a cerebral aneurysm include sudden and severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, neck pain or stiffness, blurred or double vision, sensitivity to light, and loss of consciousness. These signs may indicate a ruptured aneurysm and require prompt medical attention.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a cerebral vascular aneurysm, including a family history of aneurysms, high blood pressure, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug abuse (particularly cocaine), and certain genetic conditions such as polycystic kidney disease and connective tissue disorders.
Diagnosing a cerebral vascular aneurysm typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, cerebral angiography, and lumbar puncture. These tests help determine the size, location, and severity of the aneurysm.
While it may not be possible to prevent all cerebral vascular aneurysms, certain lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk. These include maintaining a healthy blood pressure, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress, and staying physically active.
Raising awareness about the signs, symptoms, and risk factors of cerebral vascular aneurysms is crucial for early detection and intervention. Education efforts can help individuals recognize the warning signs and seek prompt medical attention if necessary.
Recovery from aneurysm surgery depends on several factors, including the type of procedure performed, the size and location of the aneurysm, and the individual’s overall health. In general, recovery may involve a hospital stay, followed by a period of rest and rehabilitation to regain strength and function.
Cerebral haemorrhage may result from a cerebral aneurysm. Symptoms of cerebral haemorrhage include sudden and severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and loss of consciousness. Immediate medical attention is required in the event of a cerebral haemorrhage.
Treatment for intracranial aneurysms, which occur within the skull, may include surgical clipping, endovascular coiling, or flow diversion techniques to prevent rupture and reduce the risk of complications.
Screening guidelines for cerebral vascular aneurysms may vary depending on individual risk factors and medical history. However, individuals with a family history of aneurysms or certain risk factors may benefit from regular screening and monitoring.
Complications of aneurysm rupture can be severe and may include cerebral haemorrhage, brain stroke, brain damage, neurological deficits, and even death. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize the risk of complications and improve outcomes.
Aneurysm rupture is usually a life threatening event. The possibility of the survival of the patient depends only on whether the best medical or surgical treatment is available and that too in a short period of time.
Aneurysm embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a catheter into the blood vessel and using coils, glue, or other materials to seal off the aneurysm and prevent further bleeding. This procedure is often used as an alternative to surgical clipping for certain types of aneurysms.
To conclude, cerebral vascular aneurysms are a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications such as rupture and cerebral haemorrhage.
Samarth Neuro and Superspeciality Hospital has 100+ beds & specializes in emergency surgery for neurological issues/disorders & diagnostics.
Samarth Neuro and Superspeciality Hospital